ABS Edge Banding for Furniture and Cabinet Manufacturing
2026-02-12
ABS edge banding is widely used in modern furniture and cabinet manufacturing to protect panel edges, improve visual consistency, and extend service life. Made from acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, this edge banding material offers stable performance, clean processing behavior, and strong compatibility with common panel substrates such as MDF, particle board, and plywood. Its balance between durability and workability makes it a common choice for both mass production and custom projects.
Content
- 1 Material Characteristics of ABS Edge Banding
- 2 Thickness and Width Options for Different Panels
- 3 Surface Finishes and Visual Consistency
- 4 Color Matching and Customization Capabilities
- 5 Application Methods and Processing Behavior
- 6 Resistance to Moisture and Daily Wear
- 7 Comparison with Other Edge Banding Materials
- 8 Selecting ABS Edge Banding for Production Needs
Material Characteristics of ABS Edge Banding
ABS edge banding is engineered to maintain dimensional stability during processing and daily use. The material shows consistent thickness and density, which helps reduce issues such as uneven bonding or visible glue lines. Compared with brittle plastics, ABS demonstrates controlled flexibility, allowing it to follow straight or slightly curved panel edges without cracking.
From a manufacturing perspective, ABS is free from chlorine and heavy metals, which supports cleaner cutting and trimming. During edge processing, the material produces smoother edges and less powder-like residue, helping keep equipment and workspaces in better condition over time.

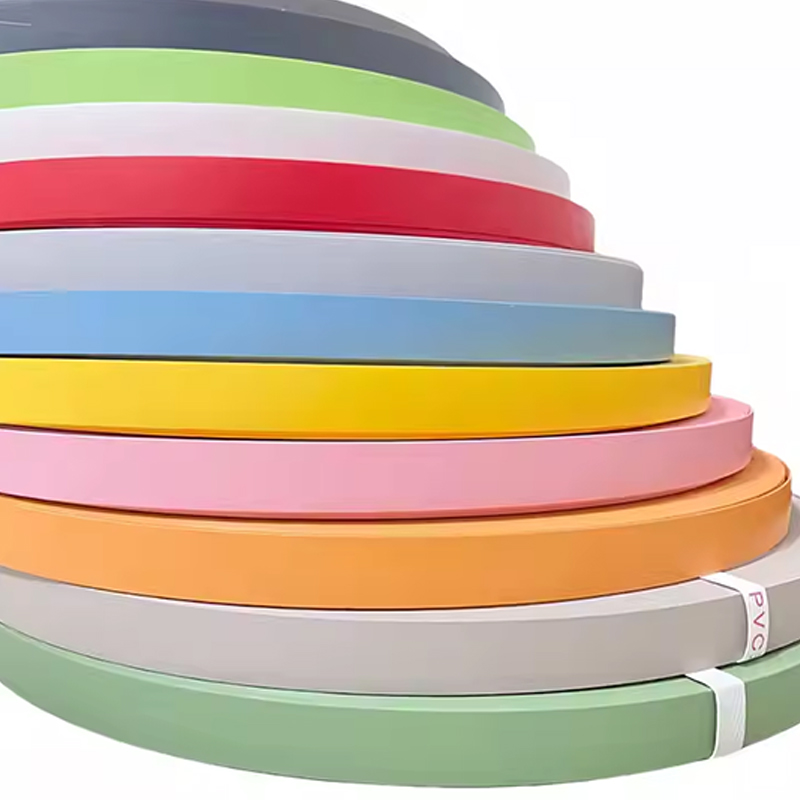
Thickness and Width Options for Different Panels
ABS edge banding is available in a range of thicknesses and widths to match different panel structures and design requirements. Choosing the correct dimensions affects both visual alignment and edge protection performance.
- Thin profiles are commonly used for lightweight panels and interior surfaces where visual continuity is the priority.
- Medium thickness options suit cabinet bodies, shelves, and office furniture that experience regular contact.
- Thicker edge banding is often applied to countertops, tabletops, and high-use edges where impact resistance matters more.
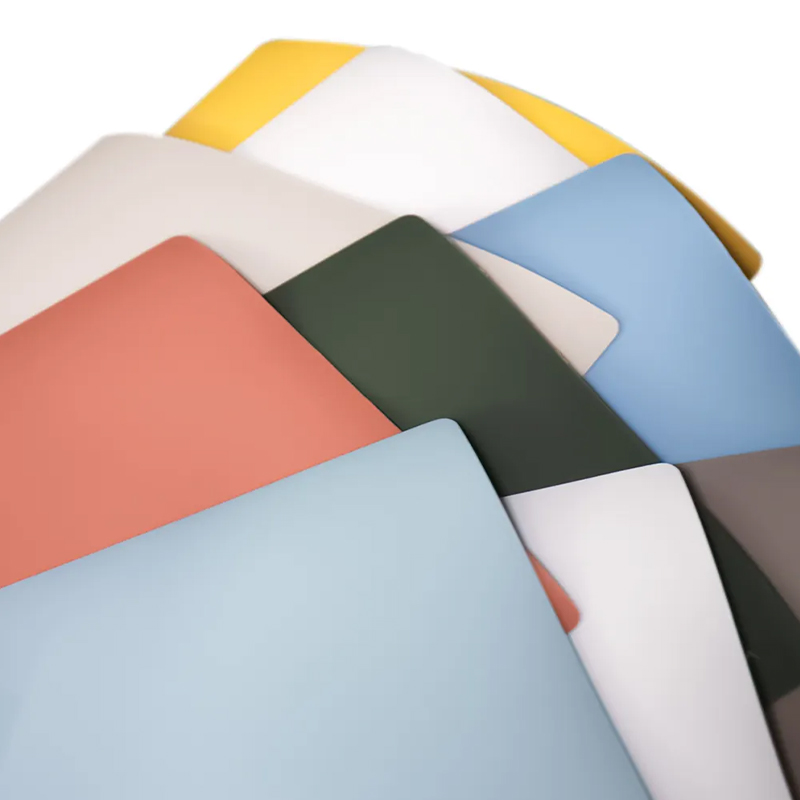
Surface Finishes and Visual Consistency
Surface finish plays a key role in how well ABS edge banding integrates with decorative panels. Manufacturers can produce smooth, matte, high-gloss, or lightly textured surfaces to match common laminate and melamine boards. Consistent surface reflection helps minimize visible transitions between the panel face and the edge.
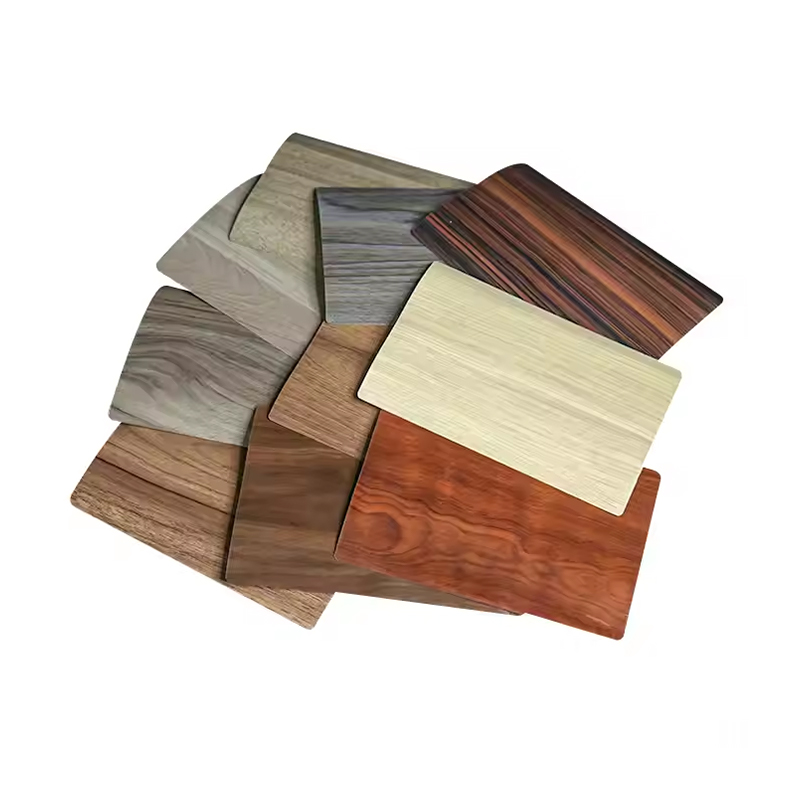
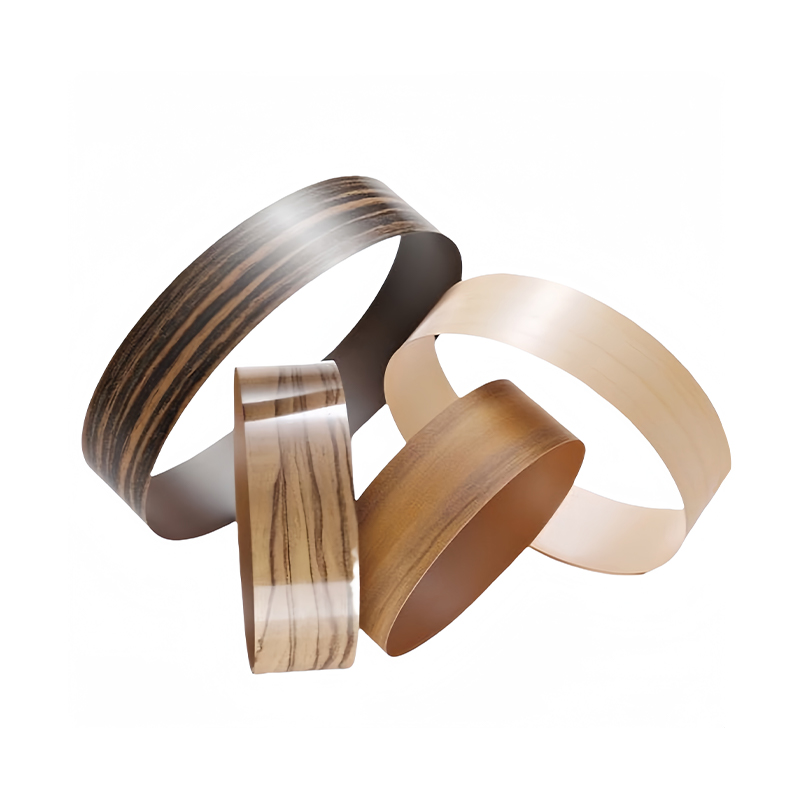
For woodgrain panels, ABS edge banding can be extruded with synchronized patterns that follow the direction of the board design. This reduces visual breaks along cabinet doors and furniture components, supporting a more unified appearance.
Color Matching and Customization Capabilities
Accurate color matching is essential when using ABS edge banding in visible furniture applications. Modern production methods allow for precise color formulation based on panel samples or standardized color systems. This helps maintain consistency across different production batches.
Customization options may include solid colors, woodgrain prints, stone-like tones, and special finishes. These options allow manufacturers and designers to align edge details with specific project requirements without altering the core panel material.
Application Methods and Processing Behavior
ABS edge banding is compatible with common edge banding machines, including manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic systems. The material responds predictably to standard hot-melt adhesives, supporting stable bonding during continuous production runs.
During trimming and finishing, ABS edges can be milled, scraped, and polished to achieve clean transitions. This controlled processing behavior helps reduce rework and supports consistent output, especially in high-volume furniture manufacturing environments.
Resistance to Moisture and Daily Wear
In interior applications, ABS edge banding offers practical resistance to moisture exposure from routine cleaning and humidity fluctuations. While it is not designed for prolonged outdoor exposure, it performs reliably in kitchens, offices, and residential furniture settings.
The surface resists common forms of abrasion from daily use, such as contact with hands, cleaning cloths, and light impacts. This helps preserve the appearance of cabinet edges and furniture profiles over extended periods.
Comparison with Other Edge Banding Materials
Understanding how ABS compares with other edge banding materials helps in selecting the appropriate option for a given project. The table below outlines general differences in performance and application focus.
| Material | Processing Stability | Visual Options | Typical Use Areas |
| ABS | Stable during cutting and trimming | Wide color and texture range | Cabinets, furniture, shelving |
| PVC | Flexible but softer during machining | Good color range | General furniture edging |
| Acrylic | Rigid, requires precise handling | High-gloss focus | Premium visible surfaces |
Selecting ABS Edge Banding for Production Needs
When selecting ABS edge banding, factors such as panel thickness, expected usage, surface finish, and color consistency should be evaluated together. Matching edge banding specifications to the production process helps improve efficiency and reduce material waste.
For manufacturers and furniture workshops, consistent quality, stable supply, and compatibility with existing machinery are often as important as appearance. ABS edge banding addresses these needs by offering predictable performance across a wide range of furniture and cabinet applications.
Recommended Articles
-
1.1 What is PP Decorative Film? PP decorative film is a type of surface material made primarily from polypropylene, a versatile and widely used thermoplastic po...
View More -
Is your furniture looking tired, outdated, or damaged? Imagine transforming it effortlessly into something stunning, durable, and uniquely yours. Enter PVC deco...
View More -
1.Introduction Edge banding is a crucial finishing process used in woodworking and furniture manufacturing to cover and seal the exposed sides of materials such...
View More


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى