Practical Guide to Lamination Film for MDF & WPC Plywood
2025-11-07
Content
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Why Choose Lamination Film for Composite Panels
- 3 Common Film Types and Properties
- 4 Surface Finishes and Textures
- 5 Application Methods
- 6 Adhesive Types and Compatibility
- 7 Key Process Parameters (Practical Ranges)
- 8 Testing & Quality Checks
- 9 Common Problems and Remedies
- 10 Handling, Storage and Environmental Controls
- 11 Selection Checklist for Buyers and Engineers
- 12 Practical Case Example
- 13 Conclusion
Introduction
This article explains practical, production-oriented guidance about Lamination film for mdf wpc plywood, including film types, surface finishes, application methods, adhesive compatibility, performance testing, troubleshooting, and a selection checklist for manufacturers and buyers. The focus is on actionable details that can be applied on the factory floor or during specification.
Why Choose Lamination Film for Composite Panels
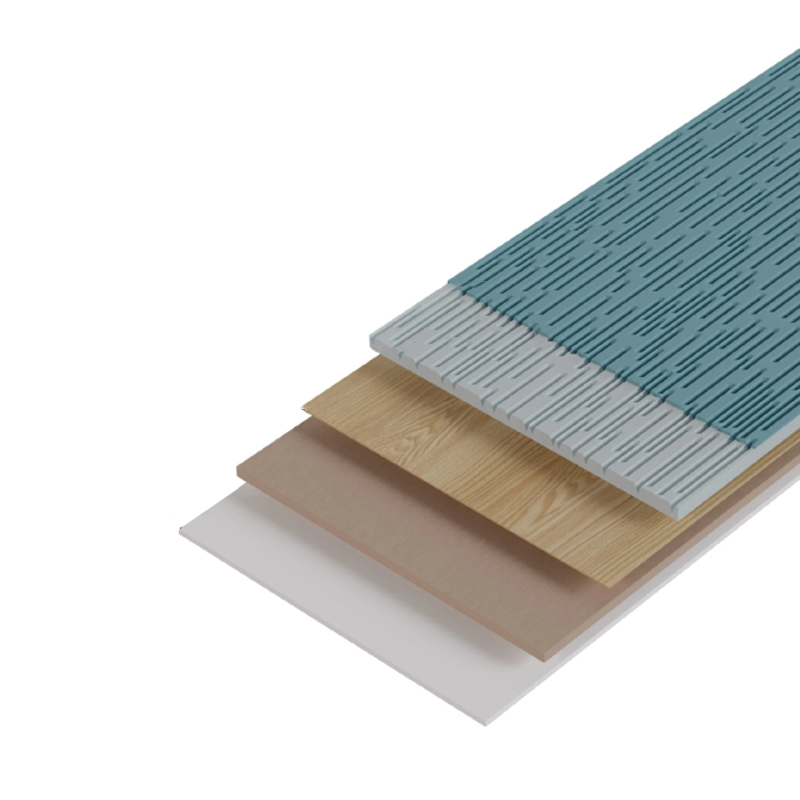
Lamination film is used to protect, decorate, and extend the service life of engineered wood panels. On MDF and WPC plywood, laminated films add abrasion resistance, moisture repellence, UV stability and decorative textures while reducing finishing steps compared with wet coatings.
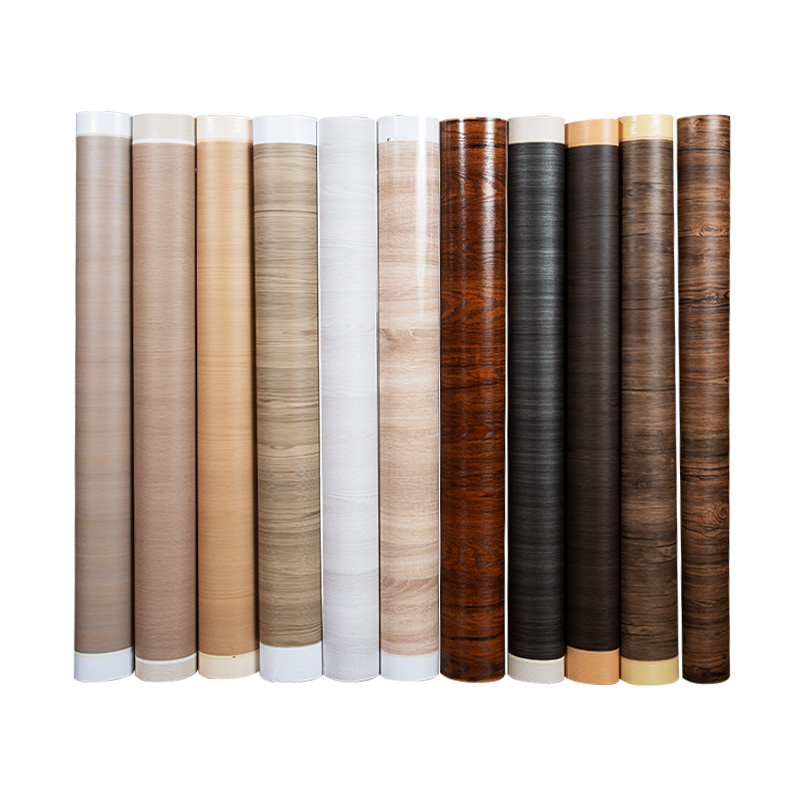
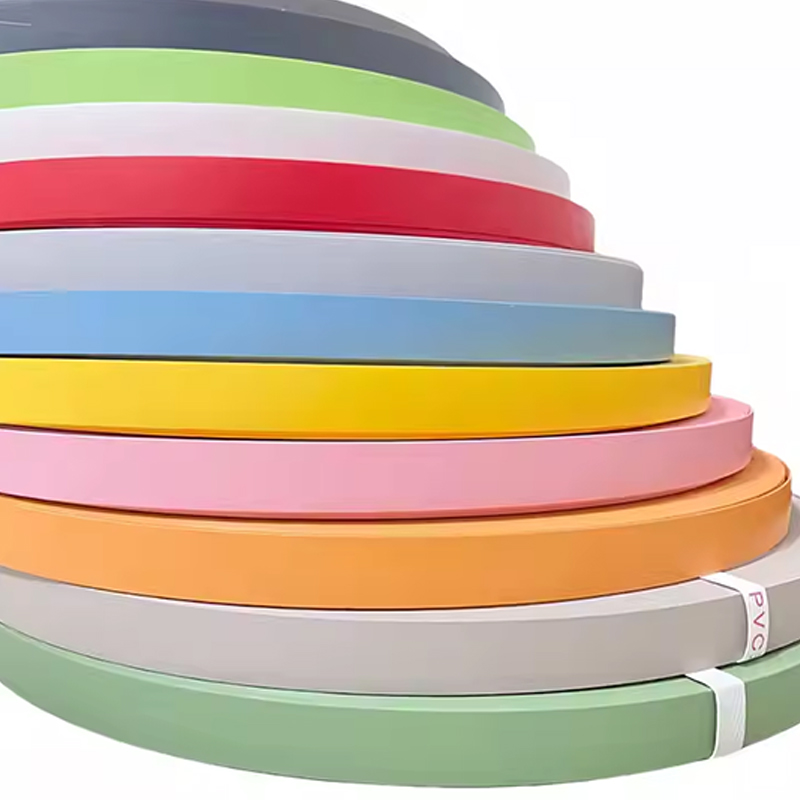
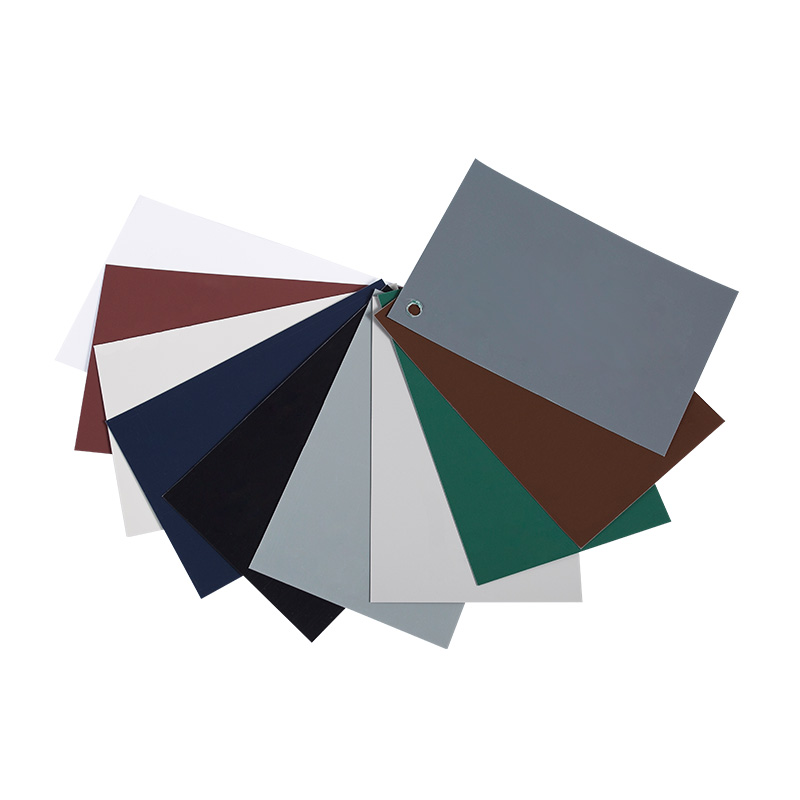
Common Film Types and Properties
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Films
PVC films are flexible and cost-effective. They are available in thin calipers (35–200 μm) for thermoforming and thicker options for edge lamination. PVC offers good printability and a wide palette of colors and woodgrain patterns.
Polypropylene (PP) and Biaxially Oriented PP (BOPP)
PP and BOPP are lighter and have superior clarity for glossy finishes. They provide lower moisture uptake than PVC and can be used where recyclability or lower VOCs are prioritized.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Films
PET films offer high mechanical strength, excellent scratch resistance and temperature stability, making them suitable for high-end surfaces and where dimensional stability is critical.
Acrylic and UV-Curable Topcoated Films
Films with pre-applied acrylic or UV-curable topcoats provide immediate surface hardness and chemical resistance after curing. These are often used in fast production lines requiring immediate handling.
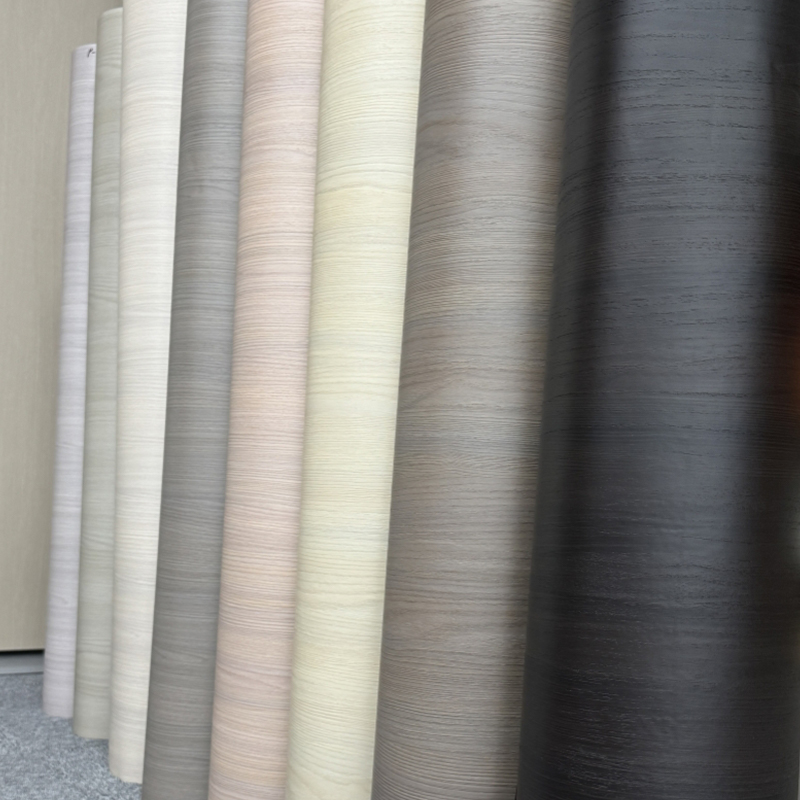
Surface Finishes and Textures
Choose finish by balancing appearance, tactile feel, and performance. Common finishes include high gloss, satin, matte, embossed woodgrain, leather-like textures, and ultra-matte anti-fingerprint surfaces.
- High gloss — visually striking, easier to clean but shows scratches and fingerprints.
- Matte / ultra-matte — hides minor scratches and marks; can be more challenging to clean.
- Embossed woodgrain — matches real wood textures, useful for furniture and cabinetry.
- Soft-touch finishes — improved hand feel for premium products; may require specific topcoats.
Application Methods
Dry Lamination (Hot Press)
Dry lamination uses pre-coated film with a heat-activated adhesive or uses separate adhesive films. Typical process: align film on panel, run through hot press at controlled temperature, time and pressure. Key control points: press temperature profile, dwell time, and nip pressure to avoid bubbles and achieve uniform bond.
Cold Roll Lamination
Cold roll lamination with pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSA) is suited for temperature-sensitive boards or small batches. Surface must be thoroughly cleaned and humidity controlled to prevent trapped moisture.
Continuous Vacuum / Thermoforming for Profiled Panels
For profiled or curved MDF and WPC parts, vacuum thermoforming combined with heated film allows the film to conform without wrinkling. Control film temperature and mold surface temperature to prevent stress marks.
Adhesive Types and Compatibility
Match adhesive chemistry to film and substrate. Common adhesives include EVA, polyurethane (PUR), hotmelt, and PSA. Each has trade-offs:
- EVA — economical, adequate for interior furniture; moderate heat resistance.
- PUR — stronger bond, better moisture and heat resistance; more sensitive to process control but recommended for high-performance applications.
- Hotmelt — fast set, useful for inline operations; check long-term creep under load.
- PSA — used in cold lamination; surface cleanliness and humidity control are critical.
Key Process Parameters (Practical Ranges)
Below are practical starting points for hot-press lamination on standard MDF/WPC panels. Final settings require trial runs based on equipment and material variations.
| Parameter | Typical Range | Notes |
| Press Temperature | 100–160°C | Depends on adhesive and film; PET higher |
| Pressure | 0.5–1.5 MPa (press) | Uniform pressure avoids delamination |
| Dwell Time | 20–90 seconds | Longer for thicker films/boards |
| Panel Moisture | 6–10% MC | Lower moisture reduces bubbles |
Testing & Quality Checks
Implement routine quality tests to validate adhesion and durability. Recommended procedures:
- Peel strength test (180° or 90°) — measures bond strength between film and substrate.
- Cross-cut adhesion and tape test — quick on-line check for coating adhesion.
- Scratch and abrasion tests (Taber) — quantify surface wear resistance.
- Humidity and boil tests — assess bond under accelerated aging.
- Dimensional stability and curl measurement — important for thin films on large panels.
Common Problems and Remedies
Bubbles or Delamination
Cause: trapped moisture, insufficient pressure, uneven heating, or incompatible adhesive. Remedy: dry panels to target moisture, verify adhesive activation temperature, increase pressure uniformly, and run test panels after adjustments.
Peel at Edges
Cause: poor edge sealing, sharp handling, or film too stiff. Remedy: use edge-banding or heat-seal edges, increase edge compression, or choose a film with suitable caliper for edge adhesion.
Surface Marks / Orange Peel
Cause: incorrect press temperature profile or film stretching. Remedy: adjust temperature gradient, reduce film tension during lay-up, and check for contaminants on press plates.
Handling, Storage and Environmental Controls
Store films in a climate-controlled warehouse (recommended 20–25°C; relative humidity 40–60%). Allow film rolls to acclimatize before opening. Keep rolls on pallets; avoid sunlight and sources of heat to prevent premature ageing of adhesives and coatings.
Selection Checklist for Buyers and Engineers
- Confirm substrate type (MDF density, WPC composition) and intended end-use (interior, wet area, exterior exposure).
- Choose film chemistry for required scratch, heat and moisture resistance.
- Match adhesive system to production method and performance targets (EVA vs PUR vs PSA).
- Request samples and run scaled production trials including peel, abrasion and humidity tests.
- Verify supplier capability for consistent color, texture repeatability and roll-to-roll quality control.
Practical Case Example
A mid-size cabinetry plant switched from solvent-based UV coating to a pre-coated PET film with a UV topcoat. Results after six months: line speed increased by 20%, waste from spraying decreased, and warranty claims for surface scratches fell. Key success factors were pilot trials, optimizing press temperature to 140°C and switching to PUR adhesive for improved moisture resistance.
Conclusion
Selecting and applying lamination film to MDF and WPC plywood requires coordinated choices across film chemistry, adhesive type, surface finish and process parameters. Use the selection checklist and tests above as a basis for trials. Small adjustments in moisture control, pressure distribution and temperature profiles often produce the best improvements in yield and long-term performance.
Recommended Articles
-
1.1 What is PP Decorative Film? PP decorative film is a type of surface material made primarily from polypropylene, a versatile and widely used thermoplastic po...
View More -
Is your furniture looking tired, outdated, or damaged? Imagine transforming it effortlessly into something stunning, durable, and uniquely yours. Enter PVC deco...
View More -
1.Introduction Edge banding is a crucial finishing process used in woodworking and furniture manufacturing to cover and seal the exposed sides of materials such...
View More


 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى